Introduction
Plasma fractionation, a cornerstone of modern medicine, plays a crucial role in numerous clinical applications across various medical fields. Derived from human blood plasma, this process involves separating plasma into its constituent components to harness specific therapeutic benefits. With advancements in technology and understanding, plasma fractionation has revolutionized healthcare by providing essential therapies for a myriad of medical conditions.
Definition
Proteins and other biological materials can be extracted from blood plasma using a technique called plasma fractionation, which is then used for medicinal purposes. Fractionation is a process used to separate and purify plasma-derived products to treat a variety of illnesses, including bleeding disorders and immunological deficits. These products include immunoglobulins, albumin, and clotting factors.
Understanding Plasma Fractionation
Before delving into its clinical applications, it’s essential to understand the process of plasma fractionation. Plasma, the liquid portion of blood, contains a diverse array of proteins vital for various physiological functions. Plasma fractionation involves separating these proteins into distinct fractions through processes like fractionation, purification, and concentration. These fractions are then utilized for therapeutic purposes, catering to specific medical needs.
Clinical Uses of Plasma Fractionation:
Plasma fractionation yields several essential therapeutic products that find application across diverse medical specialties:
Immunoglobulins (Ig):
- Derived from plasma, immunoglobulins play a crucial role in the immune system, combating infections and bolstering immunity.
- Clinical uses:
- Treatment of primary immunodeficiency disorders.
- Management of autoimmune diseases like rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus.
- Prophylaxis against infections in immunocompromised patients.
Coagulation Factors:
- Essential for blood clotting, coagulation factors are crucial in preventing and managing bleeding disorders.
- Clinical uses:
- Treatment of hemophilia and von Willebrand disease.
- Management of bleeding disorders in surgical settings.
- Prophylactic use in patients with clotting factor deficiencies.
Albumin:
- The most abundant protein in plasma, albumin plays a vital role in maintaining oncotic pressure and transporting various substances in the blood.
- Clinical uses:
- Volume expansion and resuscitation in patients with hypovolemia.
- Management of ascites in liver cirrhosis.
- blood pressure stabilisation in individuals with critical illness.
Alpha-1 Antitrypsin (AAT):
- A protease inhibitor that protects tissues from damage by inhibiting enzymes like elastase.
- Clinical uses:
- Treatment of alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency, a genetic disorder predisposing individuals to lung and liver diseases.
- Augmentation therapy to slow disease progression in affected individuals.
Benefits of Plasma Fractionation in Healthcare:
The utilization of plasma fractionation in clinical practice offers several significant benefits:
Life-saving Therapies:
Plasma-derived products obtained through fractionation provide life-saving therapies for individuals with various medical conditions, including immunodeficiencies, bleeding disorders, and autoimmune diseases.
Customized Treatments:
Plasma fractionation allows for the production of tailored therapies catering to specific patient needs, ensuring optimal treatment outcomes and minimizing adverse effects.
Improved Patient Care:
By providing access to essential plasma-derived products, fractionation contributes to improved patient care, enhancing quality of life and prolonging survival in individuals with debilitating conditions.
Enhanced Safety Profile:
Rigorous screening and purification processes employed during plasma fractionation ensure the safety and efficacy of derived products, minimizing the risk of transmitting infectious agents and adverse reactions.
Advancements in Research and Development:
Continued research and development in plasma fractionation technologies lead to the discovery of novel therapeutic products and improved manufacturing processes, expanding treatment options and driving innovation in healthcare.
Challenges and Future Directions:
- Supply and Demand Imbalance: Meeting the growing demand for plasma-derived products while ensuring an adequate supply of plasma donors poses a significant challenge.
- Cost and Accessibility: The cost of plasma-derived therapies may limit accessibility for certain patient populations, highlighting the need for affordability measures and equitable distribution.
- Emerging Infectious Risks: Ongoing surveillance and vigilance are essential to mitigate the risk of emerging infectious diseases and ensure the safety of plasma-derived products.
Looking ahead, advancements in plasma fractionation technologies, coupled with increased awareness and collaboration, hold promise for addressing these challenges and further enhancing the role of plasma-derived therapies in modern healthcare.
Growth Rate of Plasma Fractionation Market
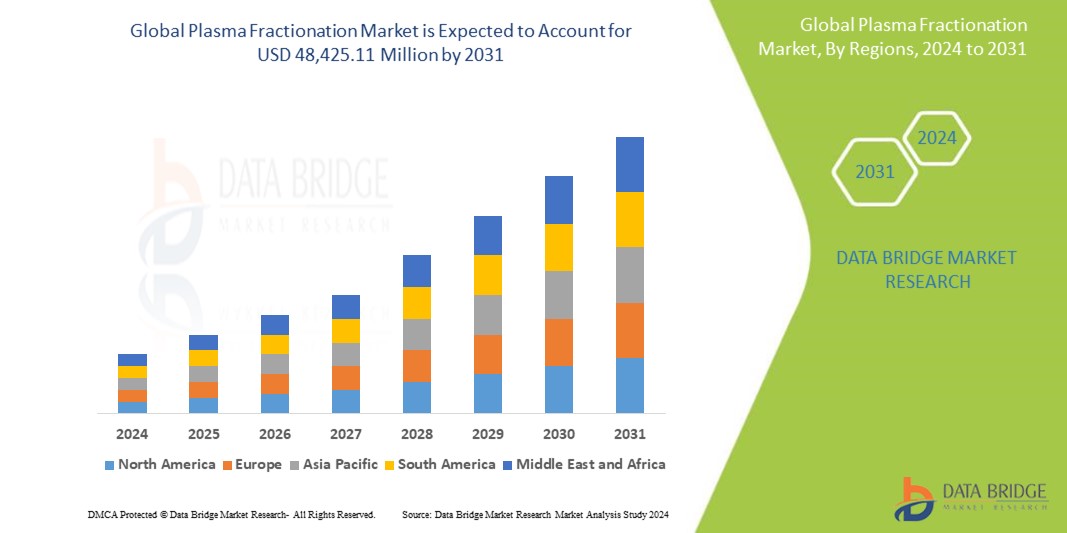
According to Data Bridge Market Research, the global plasma fractionation market is predicted to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.5% from 2024 to 2031, from an estimated value of USD 29,259.96 million in 2023 to USD 48,425.11 million by that time.
Conclusion
Plasma fractionation stands as a cornerstone of modern healthcare, offering essential therapeutic products that cater to diverse medical needs. From treating immunodeficiencies to managing bleeding disorders and autoimmune diseases, plasma-derived therapies play a vital role in improving patient outcomes and enhancing quality of life. As technology continues to evolve and research progresses, plasma fractionation is poised to remain a cornerstone of medical innovation, driving advancements in patient care and disease management for years to come.
To explore more Plasma Fractionation click here.
https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/global-plasma-fractionational-market


